Everything You Need To Know About Bats
Flittermouse is the old English name for the bat.
Flittermouse, and Everything Else You Wanted to Know About Bats
Flittermouse is an old English name for a bat that closely matches the name in Swedish and German. Bats are mammals of the Chipotera system. The word Chipotera has an ancient origin of two words in Greek, the pteron, which means hand, cheir and wing. As the name suggests, the forelegs of this mammal form webbed wings. Due to this feature, bats can fly for a long time. There are two bats, microbates and megabat low limits, both of which have more than 1,240 species. Flittermouse lives in most parts of the world, except in extremely cold regions and is ecologically and economically important in pollinating flowers, distributing fruit seeds, consuming insects, and can be harvested from caves and used as fertilizer.
Physical Description
In general, all bats have a similar shape and wing structure, but different species have finer details depending on their diet and social adaptations. The size of the bat species varies. The largest bats weigh 2.2 pounds and can have a wingspan of up to five feet. The smallest mature bats only have a six-inch wingspan and weigh approximately 0.07 pounds. Bats have mouths that are very similar to those of pointed-eared rats. Most bats have long arms and fingers attached to the leg through a thin membrane that allows them to fly. In color, they can have different shades of gray, tan or brown.
Reproduction
Most bat species have polygamy with males mating with various females. Males collect resources to attract females, and weak males live far from females. Few species, such as the Mexican free-tailed bat, are mixed, both males and females have multiple partners. As for the yellow-winged bat species, adults tend to be monogamous. In temperate regions, mating takes place in late summer and early autumn, tropical bats mate in dry seasons. Most men leave a mating plug right after the bat mating. During hibernation, mating is in torpor, and the female uses strategies to control mating, pregnancy, and timing of birth, so delivery occurs when the delivery is abundant. These strategies include delaying the fertilization of the sperm in women for months until the female is ready. Females give birth with their heads facing up, so that gravity comes into play during the process. A newborn bat puppy can be up to 40% of the mother’s weight. Depending on the species, the mother or father takes care of the younger one. Everything You Need to Know About Bats, What Can We Learn From Bats ?, Will Bats do anything in Minecraft? Are bats good luck? Are bats avoiding humans? Will bright lights keep bats away? head ?, Can I tamin a bat in Minecraft ?, Bats drop XP ?, What bats drop ?, What is a bat unique ?, What do people use for bats?, Are bats smart? Bats venom
Behavior
Bats hang upside down to hide from predators, which provides an easy take-off, as they can run with their small legs and not be able to take off like birds. While microbates are night in nature, megabates are crepular. Bats in the winter usually migrate to hibernate up to six months. They often hibernate in abandoned mines, buildings and caves in hot colonies. Because they are dependent on echolocation, bats fly in the rain because it interferes with the ability to find food. Socially, there are some species that live only in at least one million colonies. Some species share food and train young people as if strengthening social ties.
Habitat and Range
Bats scattered more than other mammals because they could fly around. In fact, the places where these mammals do not exist include the Arctic and Antarctic environments and several oceanic islands. Typically, bats are found in safe places to hide from predators and anywhere they can access food and water. These include caves, abandoned mine shafts, under bridges or structures, chimneys and abandoned buildings. But bats are not usually disturbed by humans. Depending on the species, different bats preferred winter and summer habitats
Diet
They feed on various flavors such as bats, nectar, insects, fruits, pollen and vertebrates. Megabats are mainly fed with pollen grains, fruit and nectar. They are smaller and have high metabolism because they burn energy as they move. Bats that feed on nectar have long puzzles and expandable tongues with thin hairs. Insectivorous bats feed on grasshopper, cricket, termite, bees, wasps, flies, insects and moths, among others. Other bat species feed on vertebrates, including mammals, lizards, birds, fish and frogs. Vampire bats feed only on mammalian blood like cattle. They detect this prey with their breathing and heat radiating from their bodies. In order to reduce competition with birds and avoid contact with other predators, predatory bats hunt at night, they manage to travel long distances up to 500 kilometers one night to look for food. They get their water needs from the food they eat, but some species fly non-stop and dive their tongue, getting water from lakes and streams.
How Many Species Of Bats Are There?
There are 1,240 known species of bats.
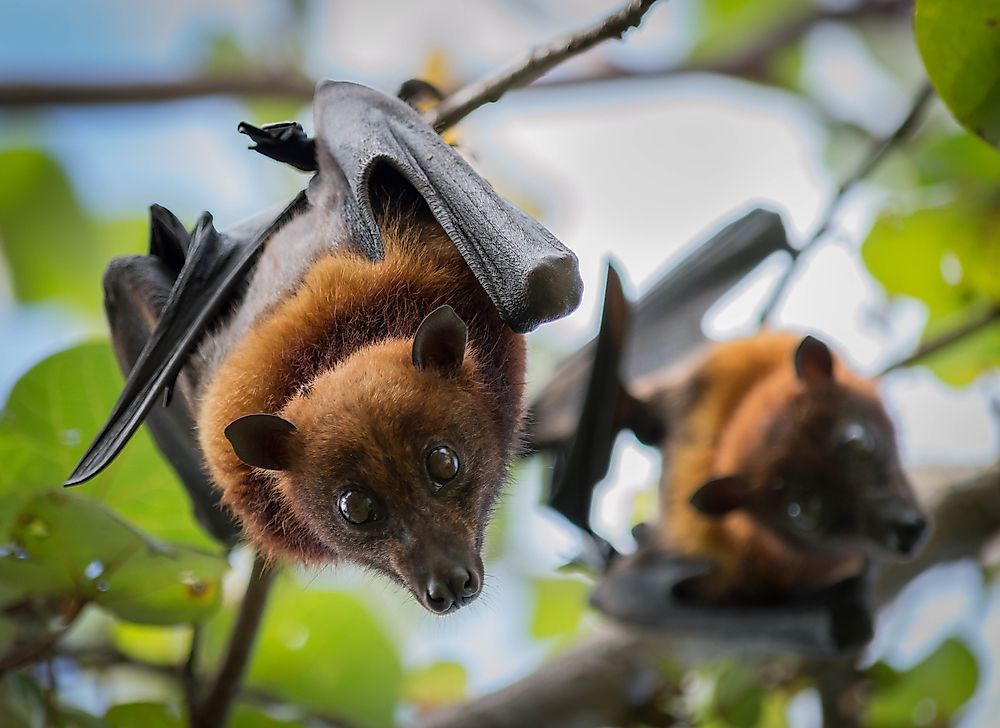

Although they resemble rodents and can fly like birds, bats are mammals with all their characteristics, including the birth of an ordinary mammal and sucking its offspring. When bats start eating food, they are active at night, dawn and twilight. Their bodies are between three and seven inches, with membranous wings between eight inches and two feet, depending on the species. They can produce a unique sound and interpret the reverb in terms of direction, distance, speed and obstacle size using their long ears. Bats are social animals and live in colonies in dark caves, old buildings, trees and tunnels.
Bat Categories
According to the order Chiroptera, there are about 1,240 bat species classified in two sub-categories: Megachiroptera (megabats) and Microchiroptera (microbates). The two categories or lower boundaries are based on the size of the bats and other unique features.
Megachiroptera
Megachiroptera is also called fruit bats due to their tendency to feed the berries. Also, the ability to interpret slightly smaller ears and sound waves is low. However, megabates have a very sharp view. Some adults will grow up to 40 meters and their wings will grow to two feet. Examples of bat families at the lower border of the Megachiroptera are the black flying fox, the Jamaican bat, the gold-hat bat, the Mexican free-tailed, short-nosed bat, and the Egyptian fruit bat.
Microchiropter to
The Microchiroptera lower bound consists of 17 bat families with relatively small and longer ears and a traction that adapts to echolocation. Although they have weak vision, they communicate through the sound waves and transmit them through the mouth or nose. They do not have claws on their second finger and have a small amount of theft. Examples of bat families in this lower border are bulldog bats, disc and pouch winged bats, brown-eared bats, horseshoe, mustache bats, cleft face and false vampire bats. Both sub regions rest upside down while resting in roosts.
World’s Largest Bat Colony
More than twenty million bats join each summer in a cave in Texas, near the city of San Antonio. Bats, mostly drawn from Mexican free-tailed bat species, fly more than a thousand miles into the 100-meter-wide cave known as the Bracken Cave every March to October. Here bats give birth to many. Protectionists prevented human intervention both on land and in the air, ensuring that there were no lights in the area. Over $ 20 million has been invested in the project. Bat Conservation International protects more than 10 million bats annually. The cave is surrounded by more than 1,500 acres of bush area to attract bats during the summer season. During this period, bats were fed with destructive insects such as army-cutting wolves and Bullworth moths and have economic value for cotton farmers.
How Many Bats Are There in the World?
Statistics showed that bats are the second most populated mammals after rodents. This means that there may be as many as a billion bats worldwide. In various seasons such as winter, it is difficult to perform a census due to its night nature and winter insomnia. The nature of torpor during seasonal migration and metabolism makes them difficult to count, especially when there is insufficient food.
How many species of bats are there?
There are 1,240 bat species known.
Where Do Bats Live?
Bats inhabit most parts of the world, except the cold polar regions.
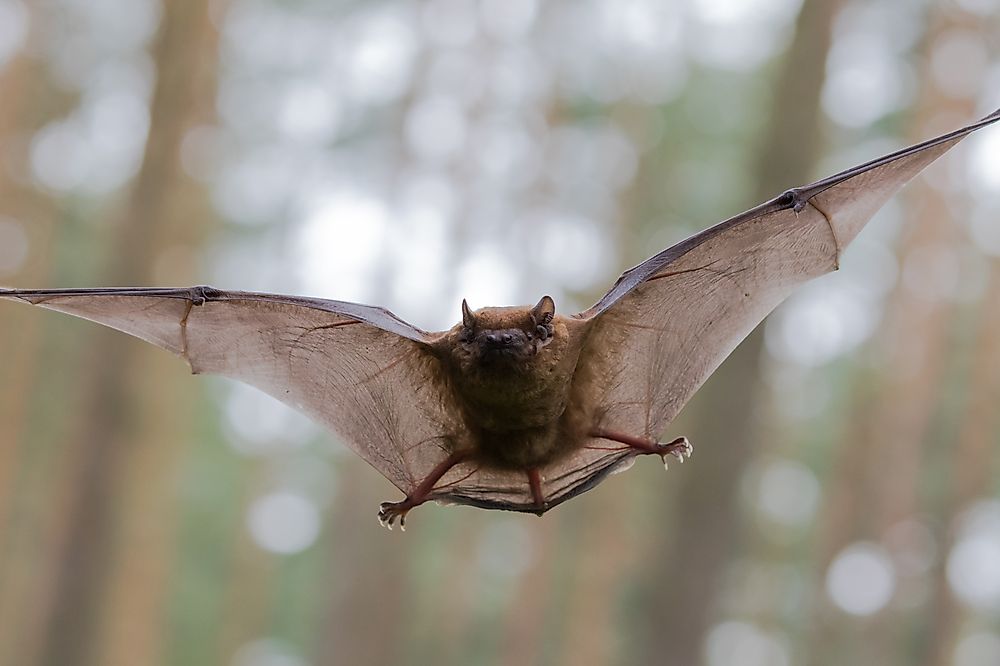

According to the latest estimates, there are currently around 1,240 bat species in the world. These unique flying mammals come in a wide variety of sizes, the smallest species weighing about 0.07 ounces, the largest weighing about four kilos. It is interesting that bats have the privilege of being the only mammal that can fly for long periods of time. Except for extremely cold environments such as the Arctic and Antarctica, bat varieties can be found worldwide. The habitats that these creatures choose to live largely depend on the types of food they eat. Research has shown that the most popular areas where bats live are tropical regions such as Central and South America, which host about a third of all bats on Earth.
Types of Bats
Bats are usually divided into two boundaries; The microbates use a natural form of bioxonar, called echo positioning, to hunt prey, while megabates feed a variety of fruit species. Most bats are nocturnal and can only be seen only during the night. Although people are often afraid of bats, perhaps because of their connection with vampires in popular books or movies, unique creatures play an important role in protecting the ecosystems they live in. Not only do the flowers serve to pollinate, but also flying mammals emit the seeds and act as a natural pest control form by eating a large number of insects.
Due to their ability to fly, bats can travel long distances to find enough food and proper shelter. Many bat species can adapt to a wide variety of different habitats based on many factors such as the time of the year, weather conditions and availability of food sources. In wild bats, they can build their roost in naturally constructed structures such as caves, leaves and trees.
Insect-Eating Bats
Bats in the northern parts of the world, as in the UK, consume diets that consist primarily of insects. In fact, 70% of bats in the world are insect eaters. One such example, the small brown bat is the most common bat type in Canada and hunts its little prey during the flight. This bat species typically ranges from 0.25 to 0.49 ounces and has a wingspan ranging from about 8.66 to 10.63 inches. The little brown bat can consume a thousand mosquitoes in just one hour.
Most insect-eating bats are known as insecticides, based only on a diet of various insects, including insects, crickets, flies, grasshoppers, termites, wasps and bees. Some common examples of insect-eating bats include the Mexican free-tailed bat, brown long-eared bat, and various types of horseshoe bats. Due to their high metabolic rate and various natural factors such as bats burning large amounts of energy during flight, these creatures should regularly consume large amounts of food. In fact, it is known that those who are fed a diet consisting primarily of insects eat in amounts equal to approximately 120% of their body weight.
Fruit-Eating Bats
Primarily fruit consuming bats are known as pharmaceutical drugs. Examples of such bat species include the Jamaican fruit bat and the tube lip nectar bat. These bats feed on ripe fruits, where they cut the trees using their teeth. Bats that feed on fruit and nectar are naturally equipped with long puzzles and languages that can be extended directly to the flowers. Fruit-eating bats play an important role in the local ecosystems in which they live, because they emit fruit and flower seeds, as well as pollinated flowers.
Jamaican fruit bats live in Greater and Lesser Antilles, including Mexico, Central and South America, as well as Cuba, Haiti, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago and the Dominican Republic. These flat-faced bat species eat a fruit-rich diet, such as figs and leaves of local plants.
Animal-Eating Bats
Several bat varieties consume vertebrates as an important part of their diet. These species include fringe-lip bat and larger night bat. These bats feed on a variety of small animals, such as birds, frogs, lizards, and fish.
The unique medium-sized fringed bat has pronounced impacts on the muzzle and lip areas. He builds his house near ponds and streams in tropical forests and builds his roost in natural structures such as caves, carved logs and trees. The diet of the fringe-lipped bat consists of lizards, frogs, insects, and even some types of fruit.
Blood-Sucking Bats
A small amount of bats consists of diets rich in animal blood. These species include vampire bats with hairy legs and white wings. These bats often feed on mammals such as cows and birds.
Hibernation, Migration, and Shelter
Although most species live in tropical areas, those living in temperate climates migrate to winter hibernation or to warmer places until warmer weather returns. Bats can occupy a wide variety of habitats, such as deserts, mountainous areas and areas near the ocean.
Bats build their houses in a place called roost. In temperate climates like England, bats require different roost environments throughout the year. Cheesecloths can be found in natural structures such as caves or in tree hollows or man-made structures under buildings and roofs. Some bats may even choose to live in underground roosts. In addition to activities such as hibernation, certain types of perches are needed during the delivery process.











Comments